Common Forces in Mechanics
Common Forces in Mechanics: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Contact Forces,Tangential Reaction Force,Tension in Strings, etc.
Important Questions on Common Forces in Mechanics
A monkey of mass is holding a vertical rope. The rope will not break when a mass of is suspended from it but will break if the mass exceeds . What is the maximum acceleration with which the monkey can climb up along the rope?
A man weighing 80 kg, stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving upwards with a uniform acceleration of What would be the reading on the scale?
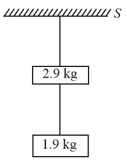
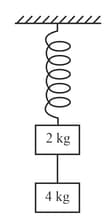
Two blocks of mass and are suspended from a rigid support by two inextensible wires each of length see figure. The upper wire has negligible mass and the lower wire has a uniform mass of . The whole system of blocks, wires and support has an upward acceleration of . Acceleration due to gravity is .
(i) Find the tension at the mid-point of the lower wire.
(ii) Find the tension at the mid-point of the upper wire.
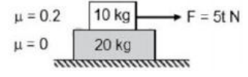
A block of mass is resting on a rough horizontal plane and is about to move when a horizontal force of is applied on it. If , find the total contact force exerted by the plane on the block.
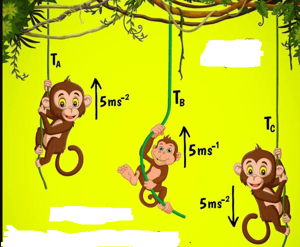
Assuming all three strings are identical, the correct order of magnitude of Tension is (Mass of all monkeys same)
The contact force between the block and the surface is
For the situation shown in the figure, horizontal spring and the spring connecting blocks and are light. The blocks and are of same mass . The pulley is smooth and fixed. The accelerations of and just after cutting the horizontal spring are
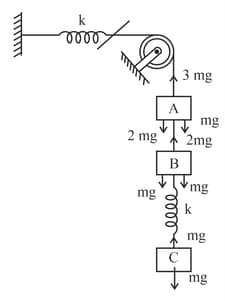
The system shown in figure is in equilibrium initially. String connecting blocks is cut at . Magnitude of the relative acceleration of blocks (in ) just after the string is cut is
Electric as well as gravitational affects can be thought to be caused by fields. Which of the following is true for an electrical or gravitational field?
The force exerted by a special compression device is given as function of compression as for , where is the maximum possible compression and is a constant. The force exerted by the device under compression is maximum when compression is:
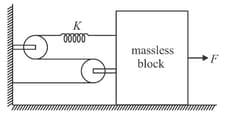
In the given diagram system is in equilibrium. If applied force is doubled how much distance, the mass less block will more towards right before new equilibrium is achieved.
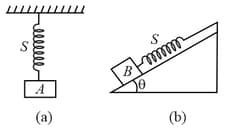
As shown in the figure, an iron block of volume is attached to a spring of unstretched length and hanging to the ceiling of a roof. The spring gets stretched by . This block is removed and another block of iron of volume is now attached to the same spring and kept on a frictionless incline plane of inclination. The distance of the block from the top along the incline at equilibrium is
Two blocks and of equal mass are arranged as shown with springs and . Spring is pulled with force . Acceleration of block is towards right at an instant. If is suddenly removed at this instant, the instantaneous acceleration of and will be (assume no friction)
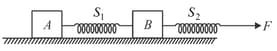
Which one of the following is not a contact force?
A uniform rope of length is on a smooth horizontal surface. It is being pulled by a horizontal force of at one end. Find the ratio of tension at a distance of from force end to tension at a distance of from free end is
A bead of mass moves along a smooth fixed ring in a gravity free region. The ring has radius . The bead is attached to a spring of force constant and natural length . The other end of the spring is fixed to a point on the ring. At an instant shown in the figure when length of spring was , force applied by the ring on the bead was zero. Rate of change of speed of the bead at this instant will be
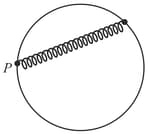
A mass of is suspended by a rope of length from a ceiling. A force of is applied in horizontal direction at the mid point of the rope. What is the angle between the rope and the vertical in equilibrium:
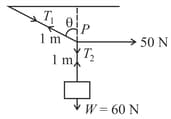
A cylinder with radius spins around its axis with an angular speed . On the inner surface, there lies a small block of mass . The coefficient of friction between the block and the inner surface of cylinder is . Find the minimum value of for which the block doesn't slip on the inner surface of cylinder. The axis of cylinder is horizontal.
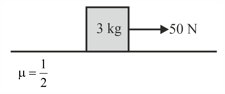
A block of mass is placed on a rough horizontal surface having coefficient of friction The magnitude of external horizontal force applied on the block gradually increases. The force exerted by the block on the surface is Match List - I with List - II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
| List – I | List – II | ||
| (P) | The magnitude of | (1) | is less than or equal to |
| (Q) | is less than of equal to | (2) | decreases gradually. |
| (R) | The angle made by with horizontal. | (3) | |
| (S) | The angle made by with vertical | (4) | increases gradually. |
Find the speed of block at the end of . Initially the system is at rest.